Review Article
Volume 3 Issue 1 - 2021
Standard Operating Procedures for Staff Training and Development
1Gentium Healthcare, Cairo, Egypt
2University of South Wales, School of Law, Accounting and Finance, Pontypridd, Wales
3McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada
2University of South Wales, School of Law, Accounting and Finance, Pontypridd, Wales
3McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada
*Corresponding Author: Mohamed Refaat, Gentium Healthcare, Cairo, Egypt.
Received: July 02, 2021; Published: September 08, 2021
Abstract
In the modern competitive work environment, staff need to constantly update their knowledge and skills to perform their jobs well. Organizations benefit from staff that feel confident in improving their efficiency and productivity, and working towards personal development. Employees also benefit from gaining new skills that improve their chances of success. This policy provides a framework for staff training to ensure that employees have the necessary competencies to deliver on assigned tasks. This policy applies to all an organization’s employees, including full-time, part-time, and supplementary employees like contractors or consultants [1]. This procedure is currently being applied to Gentium Healthcare.
Keywords: SOs; Staff Training; Development
Abbreviations: NA
Introduction
Policy Elements
Mandatory Trainings [2]
The scope of work employee’s carry-out requires certain skills that must be obtained through specific trainings. These essential trainings are mandatory and must be completed by all employees or subcontractors before they can undertake certain tasks or responsibilities. These essential trainings (and all others) can be conducted either in-house or on the premises of a third-party provider. Logs of these trainings will be recorded, kept in employment history, and be made available for audit purposes at any time.
Mandatory Trainings [2]
The scope of work employee’s carry-out requires certain skills that must be obtained through specific trainings. These essential trainings are mandatory and must be completed by all employees or subcontractors before they can undertake certain tasks or responsibilities. These essential trainings (and all others) can be conducted either in-house or on the premises of a third-party provider. Logs of these trainings will be recorded, kept in employment history, and be made available for audit purposes at any time.
Mandatory Training Curriculum [3]
The mandatory trainings must be completed by all employees within 14 days of their joining date and before taking on any responsibilities.
The mandatory trainings must be completed by all employees within 14 days of their joining date and before taking on any responsibilities.
The acting manager is responsible for securing the training materials and archiving training logs for all employees before they begin work. These records are to be kept both in the project/department file and with the QA manager.
It is the responsibility of the employee’s manager (or operations head) and the PV/QA manager to ensure trainings are completed and logs archived. These trainings will be recorded and kept in the project file and employment history and will be made available for audit purposes at any time.
Listed below are suggested mandatory trainings [4]:
| # | Training | Timeline | Schedule | Frequency afterwards |
| 1 | Data Security, Privacy and Confidentiality | Full Day | On-boarding | Quarterly |
| 2 | Pharmacovigilance & Adverse Events Reporting | On-boarding | Quarterly | |
| 3 | Interaction with Medical Professionals | Full Day | On-boarding | Quarterly |
| 4 | Business Continuity Plan | On-boarding | Quarterly | |
| 5 | All organization Standard Operating Procedures | Full Day | On-boarding | Quarterly |
| 6 | Anti-bribery Policy | On-boarding | Quarterly |
Continuous Improvement Trainings
On top of mandatory trainings, employees, managers, and Human Resource (HR) staff should collaborate to build a continuous professional development (CPD) culture to encourage the procurement of new skills. It is an employee’s responsibility to seek out new learning opportunities, a manager’s responsibility to coach their teams and identify individual needs, and Human Resources’ (HR) responsibility to facilitate staff development activities and processes.
On top of mandatory trainings, employees, managers, and Human Resource (HR) staff should collaborate to build a continuous professional development (CPD) culture to encourage the procurement of new skills. It is an employee’s responsibility to seek out new learning opportunities, a manager’s responsibility to coach their teams and identify individual needs, and Human Resources’ (HR) responsibility to facilitate staff development activities and processes.
In general, the following types of employee trainingsare most common [5]:
- Formal training sessions
- Employee Coaching and Mentoring
- Participating in conferences
- On-the-job training
As part of learning and development provisions, organizations can also arrange for subscriptions or educational material, so employees will have access to news, articles and other materials.
Individualized Trainings [6]
Employees and their managers are responsible for their continuous learning. Employee needs should be assessed on an individual basis and should include the following criteria:
Employees and their managers are responsible for their continuous learning. Employee needs should be assessed on an individual basis and should include the following criteria:
- Present job requirements
- Career Development
- Succession Planning
- Skill gaps identified by superiors
Individual trainings should focus on what employees need and how they learn best. This is why organizations encourage employees and managers to consider multiple training methods like workshops, e-learning, lectures, etc.
Employees should show willingness to improve by asking their managers for direction and advice. Managers should do the same with their own superiors, while encouraging and mentoring their subordinates. Organizations also encourage employees to use their right to self-paced learning by asking for educational material and access to other resources [7]. Examples of this kind of training and development are:
- Equal employment opportunity training
- Diversity training
- Leadership training for managers
- Conflict resolution training for employees
- Engaging experts in a field for training
Materials and Methods or Experimental Procedures
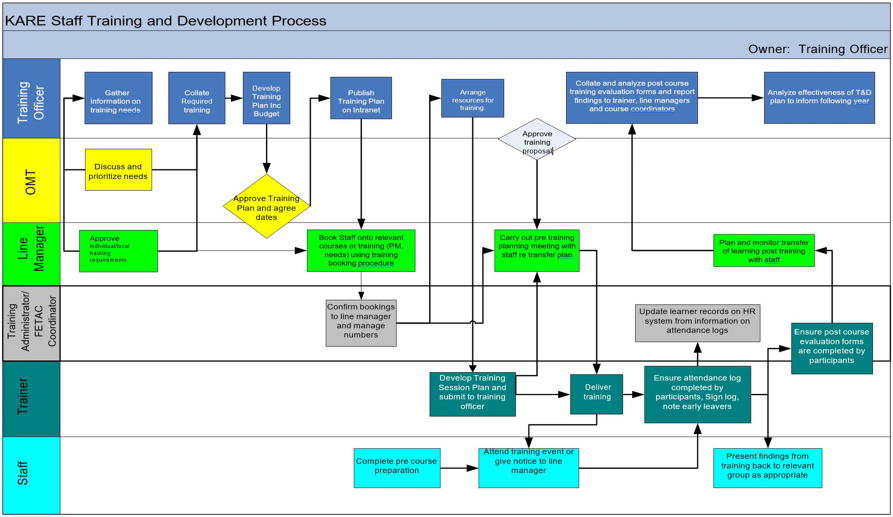
Proposed Training and Development Process [8].
The following matrix shows the duties and responsibilities within the organization for the effective and efficient flow of process.
KARE Staff Training and Development Process
Owner: Training Officer
Proposed Training and Development Process [8].
The following matrix shows the duties and responsibilities within the organization for the effective and efficient flow of process.
KARE Staff Training and Development Process
Owner: Training Officer
Process measures:
% variance expenditure versus budget re training
% training spends versus payroll
% training completed versus training planned
% variance expenditure versus budget re training
% training spends versus payroll
% training completed versus training planned
Policy Procedure
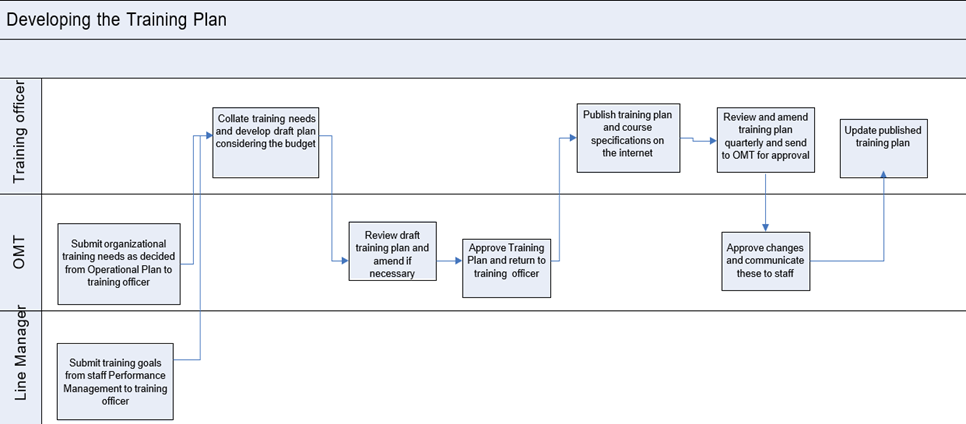
Development of training plan [9](See Appendix 1)
Development of training plan [9](See Appendix 1)
- The department manager submits training goals obtained by staff to the training officer
- The Operations Management team (OMT) identifies organization/team wide training needs based on the operation plan, and submits them to the training officer
- The Training Officer collates training needs and develops a draft plan, with budget considerations
- The OMT reviews the drafted training plan and makes any necessary amendments before approving and returning it to the training officer
- The Training Officer publishes the training plan and course specifications on the internet so they are easily accessible to staff
- The Training Officer reviews and amends the training plan quarterly and sends to OMT for approval
- The OMT approves changes and communicates changes to staff
- The Training Officer updates published training plan
Results
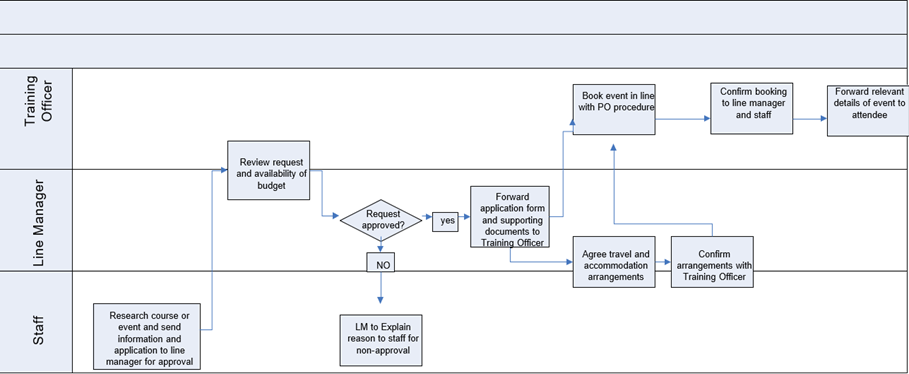
External Training Sessions [10]
This procedure should be followed when employees want to attend external training sessions or conferences: (See Appendix 2)
This procedure should be followed when employees want to attend external training sessions or conferences: (See Appendix 2)
- Employees (or their team leaders) identify the need for training based on performance, organizational or legislative changes, etc.
- Employees and team leaders discuss potential training programs and methods and come up with suggestions for future trainings.
- Team leaders contact HR and briefly present their proposal (including completed training request forms). (see appendix 3)
- HR researches the proposal, with attention to budget and training content.
- HR approves or rejects the proposal. If they reject it, they should provide employees with their reasons in writing.
- If HR approves, they will prepare dates, accommodation, reserving places, etc.
- In cases where the company does not pay for the training directly, employees will have to pay and send invoices or receipts to HR. HR will approve the employee’s reimbursement as per the invoices or receipts.
- If an employee decides to drop or cancel a training, they will have to inform HR immediately and cover any cancellation fees.
- In cases where training ends with examination, employees are obliged to submit the results. If they do not pass the exam, they will have to retake it at their own expense
- Generally, the organization will cover training fees once. They may also cover transportation, accommodation, and personal expenses, though this is left to HR’s discretion. If HR decides to cover these costs, HR should decide upon the purchased service (e.g. tickets, hotel reservations). Any other covered expenses that employees have will be reimbursed after employees provide relevant receipts and invoices [11].
- If employees want subscriptions to journals, magazines, etc., they should contact HR directly or ask their managers. Preferably, HR will set up the subscription. Though in some rare cases, HR may give formal approval to employees to do so themselves. Once employees pay for the subscription, they should inform HR of the cost and any other details in writing. Any relevant invoices should also be sent to HR [12].
Individual Development Plans [13]
Individual Development Plans should be based on analyzing training needs, talent management practices, performance reviews/appraisals, career development plans, and succession planning, as per the organization’s policy on performance management. In addition, exit interviews, staff surveys, updated job evaluations, job descriptions, individual ambitions, changing business needs, and external stakeholders’ requirements contribute to establishing Individual Development Plans that meet the needs of employees and the organization.
Individual Development Plans should be based on analyzing training needs, talent management practices, performance reviews/appraisals, career development plans, and succession planning, as per the organization’s policy on performance management. In addition, exit interviews, staff surveys, updated job evaluations, job descriptions, individual ambitions, changing business needs, and external stakeholders’ requirements contribute to establishing Individual Development Plans that meet the needs of employees and the organization.
Training Records and Documentation (See Appendix 3)
Taking the time to organize and streamline a process of documenting training records before employees begin can save time and reduce errors. From induction to comprehensive training, keeping a record of training and business-skill building is one of the best ways to gauge the training’s effectiveness, boost performance, decrease error risk, and stay in compliance with training policies [14].
Taking the time to organize and streamline a process of documenting training records before employees begin can save time and reduce errors. From induction to comprehensive training, keeping a record of training and business-skill building is one of the best ways to gauge the training’s effectiveness, boost performance, decrease error risk, and stay in compliance with training policies [14].
Starting with the basics, the following shall be included in Training Documentation and logs [15]:
- Training module name and version
- Trainee name and signature
- Instructor name and signature
- The training dates
- Training expiry date
Training documentation and logs will be recorded and kept in employment histories and will be made available for audit purposes at any point [16].
Employee Training logs will be version controlled to ensure organizations have appropriate documentation and authorization for every training program completed by each employee. Training records can also be leveraged in annual performance reviews to determine progress and company goals [17].
Evaluation
Evaluating a training’s efficacy is vital to ensuring that employees are able to meet the needs of their position and that the training budget is spent effectively. Evaluating trainings can be done using learning objectives that are decided upon prior to the learning event. This approach is qualitative and involves completing a questionnaire or report after the learning event or presentation that can be used to evaluate the training [18].
Evaluating a training’s efficacy is vital to ensuring that employees are able to meet the needs of their position and that the training budget is spent effectively. Evaluating trainings can be done using learning objectives that are decided upon prior to the learning event. This approach is qualitative and involves completing a questionnaire or report after the learning event or presentation that can be used to evaluate the training [18].
Employees are expected to use their acquired knowledge to make suggestions for changes to working practices, thus contributing to continuous improvement and showing immediate evidence of learning. Further follow-up after weeks or months can assess the training’s impact on work performance by analyzing job-specific metrics (sales, adverse events, etc.). Annual reviews provide a further opportunity to evaluate long-term impact on personal, team, and organizational objectives [19].
All development activities will be evaluated in terms of learning and impact. Prior to undertaking an activity, learning objectives will be set and after the activity learning will be evaluated using these objectives. This will be recorded on evaluation forms and also discussed with the relevant department’s manager. Long-term impact will be evaluated at performance review, in relation to attainment of performance objectives, and contribution to the organization’s goals. In addition, evaluation will assess the value of the organization’s investment in development activities. Feedback on the quality and content of training will be reviewed by the Staff Development Unit and, where relevant, internal trainers and designers [20].
HR Training Responsibilities [21, 22]
There are several tasks pertaining to employee training that fall under the responsibility of an organization’s HR department. Including:
There are several tasks pertaining to employee training that fall under the responsibility of an organization’s HR department. Including:
- Assessing training needs
- Maintaining budgets and training schedules
- Assisting with learning and development activities and strategies
- Promoting corporate training programs and employee development plans
- Calculating learning and development KPIs whenever possible and deciding on improvements
Discussion
Suggested Trainings Curriculum
It is suggested that all employees attend the following trainings, and that such mandatory attendance be included in the company’s Staff Training and Development requirements [10]:
It is suggested that all employees attend the following trainings, and that such mandatory attendance be included in the company’s Staff Training and Development requirements [10]:
| # | Training | Timeline |
| 1 | Data Security, Privacy and Confidentiality | Full Day |
| 2 | Pharmacovigilance & Adverse Events Reporting | |
| 3 | Interaction with Medical Professionals | Full Day |
| 4 | Data Backup and Disaster Recovery | |
| 5 | Business Continuity Plan | Full Day |
| 6 | Anti-bribery Policy | |
| 7 | Employee Handbook– Human Resources Policies | Full Day |
| 8 | Information Security Training | |
| 9 | Code of Ethics framework | |
| 10 | Communication skills | Full Day |
| 11 | Time management skills | |
| 12 | Presentation skills |
Conclusion
Appendix 1 [23]
Appendix 2: (External training process) [24].
Appendix 3 [25]: (Training Documentation and logs).
| Training Module | Trainee Name & Signature | Instructor Name & Signature | Training Date | Expiry Date |
Acknowledgments
Gather acknowledgements including the list of individuals who aided during the research at the end of the article in a separate section before the references.
Gather acknowledgements including the list of individuals who aided during the research at the end of the article in a separate section before the references.
References
- Employing Independent Contractors https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/employingindependentcontractors.aspx (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Identify Innovate Demonstrate Encourage Quality Improvement Training for Healthcare Professionals; (2012).
- Mandatory Training - What is Mandatory Training? - Health & Social Care Training Providers - UK Accredited https://mandatorycompliance.co.uk/2018/05/18/mandatory-training-what-is-mandatory-training/ (accessed May 13, 2020).
- CFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21.
- Michael, A. Topic Gateway Series Mentoring and Coaching Mentoring and Coaching Topic Gateway Series No. 50.
- WORKFORCE PLANNING PRACTICE; (2018).
- 5 Reasons Why Managers Should Be Involved In Employee Training https://www.efrontlearning.com/blog/2018/05/why-managers-improve-employee-engagement-training.html (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Understanding Organizational Structures https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/understandingorganizationalstructures.aspx (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Wipo. PMSDS-Guidelines (Version 2 ) Performance Management and Staff Development System.
- Human Resources Management and Training UNITED NATIONS ECONOMIC COMMISSION FOR EUROPE Human Resources Management and Training.
- Starting an HR Department from the Ground Up https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/startinganhrdepartment.aspx (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Your Employee Tested Positive for Covid-19. What Do You Do? https://hbr.org/2020/03/your-employee-tested-positive-for-covid-19-what-do-you-do (accessed May 13, 2020).
- How to Conduct a Training Needs Assessment https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/how-to-guides/pages/conduct-training-needs-assessment.aspx (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Process Improvement/Streamlining | UCOP https://www.ucop.edu/efficiency/ideas/process-improvement-streamlining.html (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Training Requirements in OSHA Standards.
- DOCUMENTATION AND RECORD KEEPING 1.0 DOCUMENTS AND RECORDS 2.0 DOCUMENTING HACCP PLANS 3.0 CREATING AN AUDITABLE PROGRAM 3.1 Document and Record Control 4.0 DOCUMENTATION SYSTEM FORMATS 4.1 Monitoring or Activity Section 4.2 Deviation Procedures and Corrective Actions.
- Managing Employee Performance https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/managingemployeeperformance.aspx (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Phelps, R. P. Synergies for Better Learning: An International Perspective on Evaluation and Assessment. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy and Practice. 2014, pp 481–493. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594X.2014.921091.
- Improvement Leaders’ Guide Improvement Knowledge and Skills General Improvement Skills.
- Darling-Hammond, L.; Flook, L.; Cook-Harvey, C.; Barron, B.; Osher, D. Implications for Educational Practice of the Science of Learning and Development. Appl. Dev. Sci. 2020, 24 (2), 97–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2018.1537791.
- Developing Employees https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/developingemployees.aspx (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Cohen, E.; Cohen, E. Employee Training and Development. CSR HR 2019, 153–162. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781351278607-11.
- How to Design Your Personal and Professional Development Program https://managementhelp.org/training/systematic/guidelines-to-design-training.htm (accessed May 13, 2020).
- Learning and Development (2015).
- What You Need to Include in Your Employee Training Log Template https://www.knowledgewave.com/blog/training-log-template (accessed May 13, 2020).
Citation: Mohamed Refaat, Marwan ElBagoury and Amy Hutchinson. (2021). Standard Operating Procedures for Staff Training and Development. Journal of Biotechnology and Immunology 3(1).
Copyright: © 2021 Mohamed Refaat. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.