Research Article
Volume 1 Issue 1 - 2019
The Importance of the Quality of Power Supply of Treating Fractures of the Bones of the Leg According to the Ilizarov Method
Russian Ilizarov Scientific Center «Restorative Traumatology and Orthopaedics. Kurgan, Russia
*Corresponding Author: Vladimir A Schurov, Russian Ilizarov Scientific Center «Restorative Traumatology and Orthopaedics. Kurgan, Russia.
Received: January 30, 2019; Published: February 08, 2019
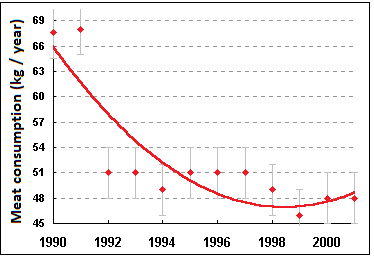
In the period from 1970 to 2008 there was a significant deterioration in the quality of nutrition of the population of the regions of Russia, in particular, according to such an important indicator as meat consumption (from 70 to 43 kg per year per person).
The dynamics of terms of fixation of fragments with closed fractures of the bones of the tibia in 1923 patients with the use of an external fixation device according to the Ilizarov method are analyzed. It is revealed that the increase in the periods of fixation of fragments, first discovered in 1976 in the group of the least socially protected people of retirement age, after 1986 became apparent in all groups of patients of working age. The increase in the duration of treatment was more pronounced in patients with more severe fragmentation fractures of the shin bones. In the current situation over the past 10 years, the transfer of patients from the 3rd week of the fragment fixation period to the outpatient treatment regimen has entered the clinical norm. At the same time, the treatment time has increased, but the period of functional rehabilitation has decreased.
Keywords: Meat consumption; Fractures of shin bones; Ilizarov method; Patient age
The role of socio-economic factors, in particular the protein-caloric value of nutrition as an essential component of the state of human reactivity, began to attract the attention of scientists as the treatment of patients improved and the economic situation of the regions improved [1]. The question of the influence of the quantity and quality of food consumed on the fusion dynamics of damaged bone is not as simple as it might have seemed in the first approximation. The fact is that bone fractures grow together even in conditions of complete starvation [2]. Apparently, the organism in the course of previous life activity creates an emergency supply of necessary plastic materials, sufficient for fusion of an uncomplicated fracture. And only with chronic protein and vitamin deficiency, bone fusion slows down [3, 4].
In this case, the mechanical strength of the bone regenerate in experimental animals is insufficient. The protein deficiency of the organism can be judged on the basis of biochemical studies of the content in the blood plasma of albumin and globulins, as well as by the level of hemoglobin. It turned out that the hemoglobin content in the blood is interconnected with the results of treatment of trauma patients [5]. The lack of protein nutrition is unfavorable for bone consolidation [6], especially during long-term healing of bones in the hip joint [7].
With the elimination of the harmful effects of chronic protein deficiency, the consolidation of fractures of the long bones of the limbs is accelerated [8]. There is a large literature describing the importance of nutritional supplements and vitamin D3 for bone consolidation [9], especially in the elderly [10], in particular, in lean elderly women with hip fractures [11]. Describes the decrease in the loss of bone substance in the proximal with fresh injuries [12]. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the quality and relevance of nutritional supplements to the needs of the body after a fracture [13].
Consequently, for reparative regeneration, the quality of life in the period of time (about 3 years) preceding the injury is of greater importance [2, 3, 6, 8]. In practice, a traumatologist often has to answer the question about the effect of alcohol consumption on fracture healing. In this question, the opinion of researchers is controversial, since age groups with full and incomplete nutrition were not distinguished. It is well known that alcohol is an active chemical that is not indifferent to the body. Experimental conditions in rats have been proven, with chronic and excessive alcohol consumption suppresses the reparative process in the damaged bone [14-16].
The aim of the study was to identify deterioration in the quality of nutrition of various groups of the population for the duration of the period of fixation of bone fragments under conditions of standardized treatment according to the Ilizarov method.
Material and Research Methods
Patients were treated in the Department of Traumatology No. 1 of the Laboratory of Acute Injury of the Russian Scientific Center Restorative Traumatology and Orthopedics named after Acad. G.A. Ilizarov using methods of transosseous compression osteosynthesis.
The archive material is analyzed - 512 case histories of patients with closed helical and comminuted fractures of the bones of the leg, who were treated at the clinic of the Scientific Center from 1970 to 2008.
A total of 641 patients were examined, who were treated at the RSC “VTO” for a closed diaphyseal fracture of the bones of the leg. All patients examined in history did not have concomitant chronic somatic diseases. In addition, when drawing up the curve of the dynamics of fixation dates for previous years, the results of the analysis of the terms of treatment of 770 patients presented in the works of other authors [17] were taken into account. As a control group 208 healthy people were examined.
Physiological examination of patients was carried out after a period of adaptation for 5-7 days after surgery with an interval of 14 days. The frequency of examinations averaged 3-4 for the period of inpatient treatment. Statistical processing of the results was carried out using the methods of variation statistics with the definition of parametric t - Student's criterion, correlation and regression analyzes [18]. Standard statistical programs used in the Microsoft Excel editor were used. The paper presents the arithmetic average M, the error of the mean - m.
Results of Research
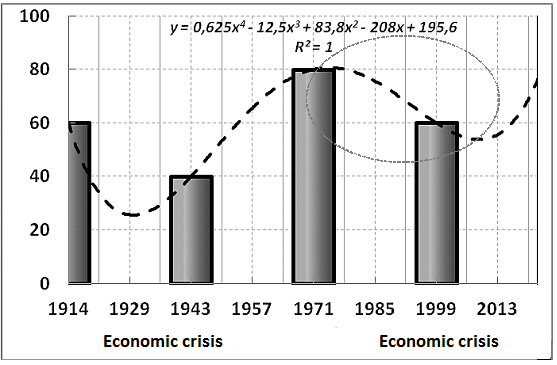
At the beginning of the last century, the Russian economist N. K?ndratiev [19] discovered the cycles of the world economy recurring every 50 years. We are witnessing the finale of the 5th cycle (Figure 1). With the mathematical approximation of the reference points of this cycle by a regression equation of level 4, unfortunately, a phase of decline in indicators is revealed that go beyond the critical values of the state of the economy of the Kurgan region.
More than 50 years ago, a new Ilizarov osteosynthesis technology was introduced into clinical practice, which made it possible to significantly reduce the time and improve the outcome of treatment of patients. The Ilizarov method has gained wide international recognition [17].
At that time, clinical success in treating patients contributed significantly to the neglect of the role of a number of biological and socio-economic factors in determining the rate of reparative regeneration. Indeed, relatively severe fractures grew together in a time comparable to the duration of treatment of patients with closed helical and oblique fractures. In terms of applying the Ilizarov treatment method, the age of patients also did not have a significant effect on the timing of the fracture of a broken bone.
At that time, clinical advances in treating patients largely contributed to the neglect of the role of a number of biological and socio-economic factors in determining the rate of reparative regeneration. Indeed, relatively severe fractures have grown together in a time comparable to the duration of treatment of patients with closed spiral and oblique fractures. In terms of applying the Ilizarov treatment method, the age of patients also did not have a significant effect on the timing of the fracture of a broken bone.
However, after 1990, a gradual increase in the duration of treatment of patients became apparent and the more, the more severe the injury, the greater the displacement of bone fragments and the age of the patients (Figure 2). When all the conditions of the osteosynthesis technology are fulfilled, such an increase in the duration of treatment required an explanation. The versions put forward about the overwhelming nature of the increase in the terms of treatment of patients in previous years did not confirm or could not have a decisive influence on the revealed tendency.
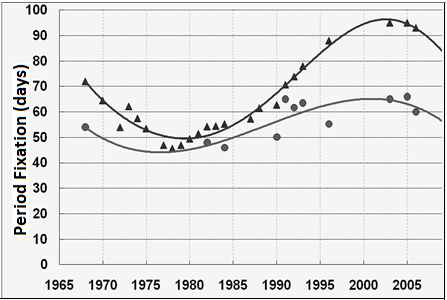
Figure 2: Dynamics of the duration of the fixation period in the treatment of patients with comminuted and helical fractures of the bones of the leg.
The increase in the terms of inpatient treatment of patients was contrary to the principles of insurance medicine, aimed at reducing costs in treating patients. The solution was found in the early transfer of patients to the outpatient treatment regimen.
The identification of facts of deterioration in the quality of life of the population of Russia, and especially of the Kurgan region, an increase in the morbidity and mortality of the population, a decrease in the birth rate, a slowdown in the growth and development of children was the reason for a more detailed assessment of the dynamics of treatment periods for patients with closed fractures of the leg bones.
If we analyze the dynamics of profit and loss of the population of the Kurgan region, reflecting the change in the socio-economic conditions of the population, as well as the dynamics of protein intake of animal origin, we observe a decrease in the corresponding graphs. Thus, the consumption of meat by residents at the hygienic rate of 90 kg decreased on average to 45 kg per person per year (Figure 3). The average per capita cash income in the Kurgan Region was the lowest in the Urals Federal District, and the families ’diet was mainly carbohydrate-containing foods: potatoes, bread products and confectionery products [20].
It has been established that the time limits for fixation have increased especially sharply among the socially unprotected segments of the population (disabled people, pensioners, and students). When the mathematical analysis of the curves of fixation of fractures in different years, it is possible to reveal their wave-like character with a period of about 50 years. Such a coincidence with the duration of the large Kondratieff cycles of economic development of the country leaves no doubt that the basis for the studied periodic changes is the trend for the entire population as a whole.
It should be noted that the nutrition of trauma patients in the hospital of our Center fully complies with hygienic standards. It is also important to note that the increase in terms of fixation in patients of different ages did not begin at the same time, but depended on the accumulated structural reserves of adaptation of the organism, which turned out to be the lowest among people of retirement age, then in patients over 40 and young students. This unequal dependence of the body resistance of patients of different ages to the deterioration of living conditions confirms the role of food quality and adaptation reserves in changing the duration of the fixation period.
It was found that already after 1979 and over the next 25 years, the periods of fixation of the bones of the leg in patients with comminuted fractures increased by 111% (p£ 0.001). At the same time, the difference in terms of fixation of comminuted and helical fractures of shin bones increased (Figure 4).
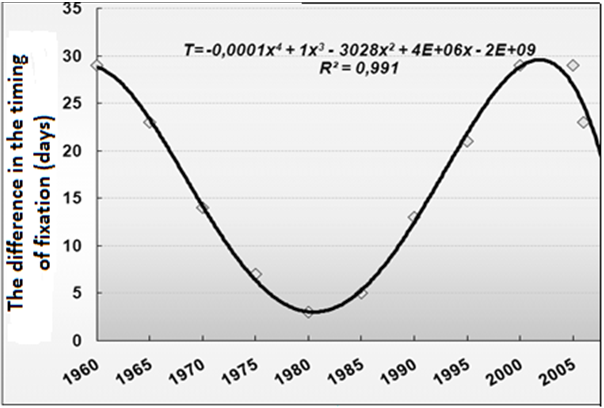
Figure 4: The difference in the timing of fixation of bone fragments in patients with closed comminuted and helical fractures of the bones of the leg.
The period of the minimum periods of treatment in patients with comminuted fractures of the bones of the tibia of different ages did not end at the same time and depended on the structural reserves of adaptation. The increase in terms of fixation in patients older than 60 years began in 1973, in patients 40–59 years old - in 1980, in children and adolescents - in 1981, in patients 20–29 years old - in 1985, and in patients 30-39 years old 1986 (Figure 5).
It should be noted that in human ancestors at bipedium, trauma with fracture of limb bones led to a loss of ability to independently obtain food, and the fusion could be carried out solely by mobilizing structural reserves of adaptation, which are reduced in the elderly and insufficient in a growing organism. By the way, in the conditions of economic stratification of the society, the most vulnerable people with a reduced level of mineral density of the skeleton bones are the most vulnerable with injuries.
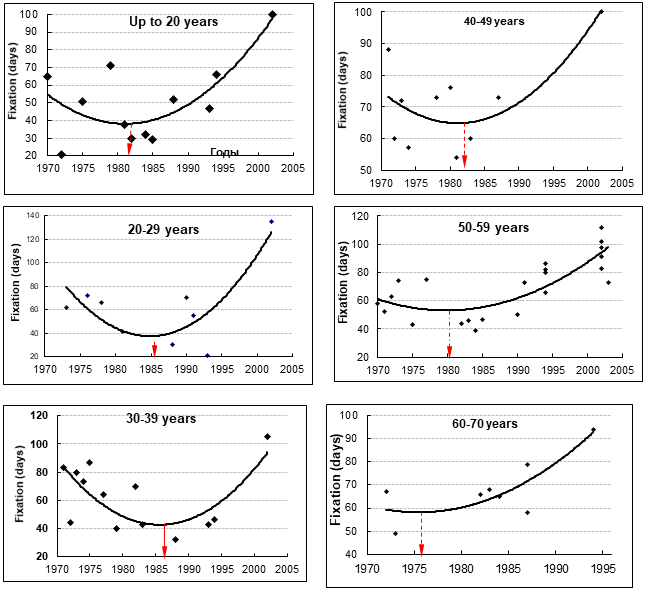
Figure 5: Dynamics of the duration of fixation in the treatment of patients with closed comminuted fractures of leg bones of different ages.
With closed spiral fractures of the bones of the lower leg, the fixation dates for the last 15 years increased by 32% (from 50 ± 5 to 66 ± 3 days). In 1990-1998, the duration of treatment of patients was directly dependent on their age, and for every 10 years of life, the fixation period increased with helical fractures for 2 days, and for comminuted fractures for 3.3 days (Figure 6).
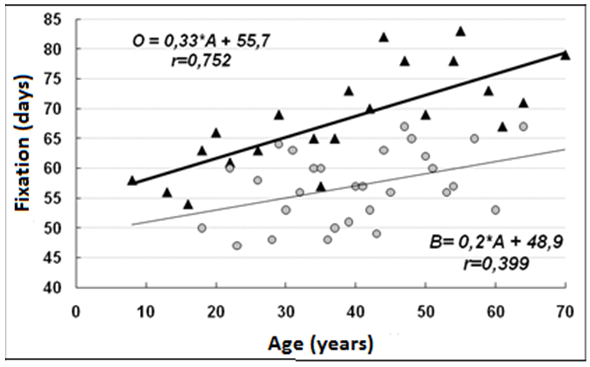
Figure 6: Age dynamics of the duration of the fixation period in helical (B) and comminuted (O) fractures of the shin bones.
Thus, deterioration in the quality of nutrition of the population, in particular, reducing the minimum level of the norm of essential proteins of animal origin by 2 times, leads to an increase in the duration of treatment of patients, especially with severe, comminuted fractures of the bones of the leg, and the more, the smaller the structural reserves of adaptation in humans retirement age. In the period of deterioration of the quality of life of the population, the role of external stimulating effects on the process of reparative bone regeneration becomes less significant.
References
- Solovyov V.S., Solov'eva S.V., Naimushina A.G., Novoselova T.V. (2004). The prevalence of pathology of the cardiovascular system and borderline neuropsychic disorders in people of working age working in various enterprises of Tyumen. // Bulletin of the Tyumen State University, ? 3. S. 120-123 (in Russ.)
- Cederholm T., Hedstrom M. (2005). Nutritional treatment of bone fracture. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, 8. No 4. P. 377-381. Review.
- K.J. Koval, S.G. Maurer, E.T. Su et al. (1999).The effects of nutritional status on outcome after hip fracture. J Orthop Trauma, 13, No 3, ?. 164-173.
- D. Pollak, Y. Floman, A. Simkin et al. (1986). The effect of protein malnutrition and nutritional support on the mechanical properties of fracture healing in the injured rat. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. Nov-Dec. 10 (6).564-567.
- K.I. Gruson, G.B. Aharonoff, K.A. Egol et al. The relationship between admission hemoglobin level and outcome after hip fracture. J. Orthop Trauma. 2002. Jan. 16 (1). 39-44.
- R. Guarniero, T.E, de Barros Filho, U. Tannuri et al., (1992). Study of fracture healing in protein malnutrition. Rev Paul Med., V.10, No 2, P. 63-71.
- Heaney R.P. Hip fracture: a nutritional perspective. (1992). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. Jun. 200 (2). 153-156.
- Day S.M, De Heer D.H. (2001). Reversal of the detrimental effects of chronic protein malnutrition on long bone fracture healing. J. Orthop Trauma, V.15, No 1, P. 47-53.
- Doetsch AM, Faber J, Lynnerup N, Watjen I, Bliddal H, Danneskiold-Samsoe B. (2004). The effect of calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation on the healing of the proximal humerus fracture: a randomized placebo-controlled study. // Calcifieta Tissue Int. Sep; 75 (3):183-188.
- Avenell A., Handoll H.H. “(2005). Nutritional supplementation for hip fracture aftercare in older people // Cochrane Database. Syst Rev. Apr 18; (2):CD001880. Review.
- Tidermark J1, Ponzer S, Carlsson P, Söderqvist A, Brismar K, Tengstrand B, Cederholm T. (2004). Effects of protein-rich supplementation and nandrolone in lean elderly women with femoral neck fractures. J. Clin Nutr. Aug; 23(4). 587-96.
- Perkins R., Scirving A.V. (1987). Callus formation and the Rate of Healing of Femoral Fractures in Patients with Head Injuries. //J. Bone Jt Surg., Vol. 69B. N 4. P. 521-524.
- Bruce D, Laurance I, McGuiness M, Ridley M, Goldswain P. (2003). Nutritional supplements after hip fracture: poor compliance limits effectiveness. Clin Nutr. Oct. 22(5). 497-500.
- Chakkalakal D.A., Novak J.R., Fritz E.D. (2005). Inhibition of bone repair in a rat model for chronic and excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol. Jul. 36 (3). 201-214.
- Elmali N, Ertem K, Ozen S, Inan M, Baysal T, Guner G, Bora A. (2002). Fracture healing and bone mass in rats fed on liquid diet containing ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. Apr. 26 (4). 509-513.
- Popova L.A. The terms of the rehabilitation treatment of fractures of the limbs by the method of transosseous osteosynthesis according to Ilizarov (clinical and statistical study). // Travmatol. Orthopedist. Russia, 1994. -? 2. –C. 54-61.
- Lakin T. F. Biometrics. Moscow.: High School, 1980. p. 293. (in Russ.).
- Kondratyev N.D. Large conjuncture cycles and prediction theory. Moscow. Publishing House Economics. 2002. 767 p. (in Russ.)
- Kremlev N.D. Problems of poverty in the Kurgan region. // Kurgan, 2004, 84 p.(in Russ.)
Citation: Vladimir A Schurov and Iliya V Schurov. (2019). “The Importance of the Quality of Power Supply of Treating Fractures of the Bones of the Leg According to the Ilizarov Method”. Journal of Medicine and Surgical Sciences 1.1.
Copyright: © 2019 Vladimir A Schurov. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.