Short Communication
Volume 3 Issue 1 - 2021
Mast Cell Carcinoma of Maxillary Sinus
ENT Department, Faculty of medicine, University Badji Mokhtar Annaba 23000 Algeria
*Corresponding Author: Smail Kharoubi, ENT Department, Faculty of medicine, University Badji Mokhtar Annaba 23000 Algeria.
Received: July 10, 2021; Published: July 21, 2021
Clinical Case
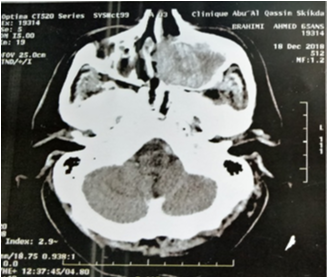
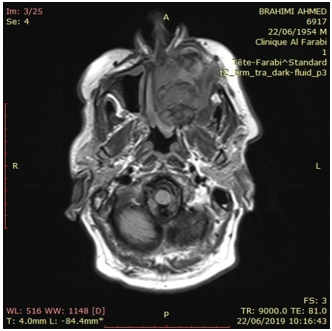
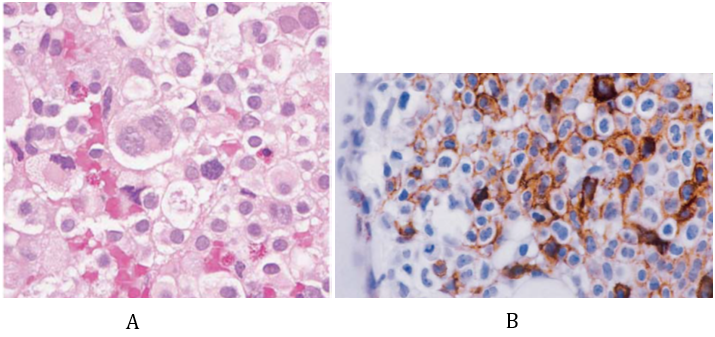
A 66 year old man presented to our ENT department with left chronic nasal obstruction and left jugual sweeling without pain. The left jugual fossea was enlarged with a firm and unlimited mass 40X25 mm. Testing of trjigeminal nerv (V) was normal. Nasal endoscopy showed deformity of left nasal lateral wall without endonasal tumor.Facial CT Scan revealed a soft tissue most of left maxillary sinus with osteolysis (anterior pars of sinus). RMN a low intensity (T1) intra sinusal mass enhancement after gadolinium .biological evaluation note normochromic anemia (hemoglobin 8, 9 g/dl) and a normal WBC and platelet count, blood glucose 1, 05 g/l. The rest of the patient’s workup liver and kinder function was negative. A Rouge Denker technique (sub labial) approach was choosed with tumor extirpation and medial maxillectomy.The diagnosis of mast cell sarcoma was confirmed after immunohistochemical who’s expressed CD117 and CD 68. Radiotherpy (50 Gy) has been proposed. The follow-up is well after 14 month later.
Mast cell sarcoma is a rare form of mastocytosis caracterized by destructive infiltration and metastatic potentiel. The most organ involved was bone (78%), gastro intestinal tract (37%), nodes (30%), skin (30%) spleen (26%), liver (20%).
A few cases of ENT localisation where reported: laryngeal (sub glottic), ear, tonsillar and lip.
Mast cell sarcoma is generally manifested by solid tumor and me be associated with fever, flushing, diarrhea and malaise.
Biological features note anemia and increased serum tryptase levels in the majority of cases. Imaging (CT and RMN) was performed to screening the tumor and loco regional extending. FDG-PET Scan can to be useful for diagnostic and therapeutic assessement [1].
Surgery is indicated especially in localized disease (total exision or debulking). Radiotherapy also has been proposed for localized disease 40 to 59 grays or in post operative with temporary efficacy. Corticosteroids improvre clinical symptoms with transient effect.Interferon-alpha, cladribine, 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine, tyrosine kinase inhibitors and targeted therapies (imatinib, desatinib, midostaurin, masitinib) may to proccure positiv response in some cases. Combinaison chemotherapy may to benefict in some patients [2, 3]. Prognosis is poor and mast cell leukemia is noted in 50% of cases.
Conflicts of Interest: No conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
References
- Monnier J, Georgin-Lavialle S, Canioni D, Lhermitte L, Soussan M, Arock M and AL. (2016). Mast cell sarcoma: new cases and literature review. Oncotarget. 7(40): 66299-66309.
- Weiler CR, Butterfield J. (2014). Mast cell sarcoma: clinical management. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 34(2): 423-32.
- Ryan RJH, Akin C, Castells M, Wills M, Selig MK, Nielsen GP, et al. (2013). Mast cell sarcoma: a rare and potentially under-recognized diagnostic entity with specific therapeutic implications. Modern Pathol. 26: 533-43.
Citation: Smail Kharoubi. (2021). Mast Cell Carcinoma of Maxillary Sinus. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Diseases 3(1). DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.5145289
Copyright: © 2021 Smail Kharoubi. von Borstel. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.